Organizational Barriers to Communication: Causes & Solutions
Communication within any organization is the foundation for reaching goals, building a healthy culture, and achieving strong performance. Yet, many businesses struggle because organizational barriers to communication get in the way. These obstacles can take many forms, from a confusing hierarchy and unclear policies to technological issues, semantic barriers, or even information overload. Addressing these barriers is essential for effective communication, employee morale, and overall organizational success.
Communication within any organization is the foundation for reaching goals, building a healthy culture, and achieving strong performance. Yet, many businesses struggle because barriers of communication can get in the way, affecting everything from productivity to employee engagement.
Contents
- 1 What Are Organizational Barriers to Communication?
- 2 Common Organizational Barriers
- 3 Organizational Barriers Examples
- 4 Effect of Communication Barriers on the Workplace
- 5 How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Communication
- 5.1 Foster Open Communication Channels
- 5.2 Clarify Communication Policies
- 5.3 Simplify Language and Avoid Jargon
- 5.4 Leverage Technology Effectively
- 5.5 Combat Information Overload
- 5.6 Break Down Departmental Silos
- 5.7 Provide Communication Skills Training
- 5.8 Enhance Leadership and Management Support
- 5.9 Address Psychological Barriers
- 5.10 Monitor and Improve Communication Effectiveness
- 6 Conclusion
What Are Organizational Barriers to Communication?
Organizational barriers are defined as obstacles within a company or workplace that hinder the flow of communication. These barriers can stem from various sources—culture, structure, technology, or even psychological factors. Understanding organizational barriers is crucial for effective communication within an organization because these challenges can significantly impact productivity, employee engagement, decision-making, and goal setting.
Common Organizational Barriers
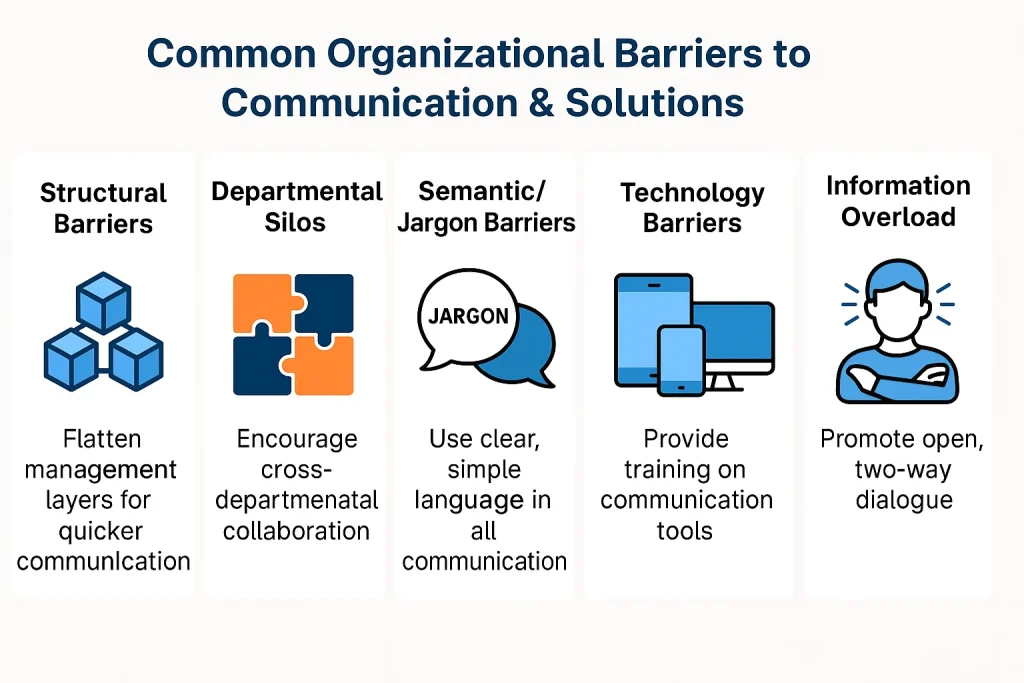
Structural Barriers
Organizational structures can create roadblocks that make it hard for information to travel from one level to another. When there are too many management layers, the message may lose its meaning, or never reach the right person at all. Ineffective communication channels, such as a lack of transparent communication channels or poor internal communications systems, only make things worse. Hierarchy and unclear roles can often be the root causes of organizational barriers.
Departmental Silos
Departments often operate in isolation, making it difficult to collaborate and share news or business communication. These silos limit teamwork and can reduce innovation, as valuable information is kept within one part of the organization rather than shared with everyone who might benefit.
Semantic Barriers and Jargon
Semantic barriers arise when employees use language, jargon, or technical terms that are not understood by everyone. This can cause misunderstandings and confusion, especially in organizations with a diverse culture or workforce from different backgrounds. For instance, an IT team might use technical language in an email that the finance team doesn’t fully understand, causing project delays.
Technological Barriers
Technology is essential for effective communication in modern organizations, but it can also become a barrier. Outdated telecommunications systems, lack of training on new tools, or using too many platforms at once can disrupt the overall communication environment. Emails, telephone calls, and digital news feeds are useful, but if not managed well, can overwhelm employees or lead to missed information.
Information Overload
Information overload occurs when employees receive too many messages, emails, or updates in a short time. This can result in lack of attention, missed deadlines, and reduced productivity. It’s important for management to set clear communication policies to ensure only essential information is sent out, helping improve their communication environment.
Psychological and Emotional Barriers
Psychological barriers, such as lack of confidence, fear of negative feedback, or past negative experiences, can hinder open dialogue within an organization. Emotions like anxiety, stress, or low morale also affect how employees perceive and respond to messages. Employee morale and engagement are closely tied to the effectiveness of communication channels and the ability to express concerns freely.
Cultural Barriers
Organizational culture and individual backgrounds can cause communication to break down. Different perceptions, values, and expectations can affect how messages are sent, received, and interpreted. A culture that doesn’t promote open communication channels will face more misunderstandings, lower employee engagement, and an overall decrease in organizational performance.
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers include office layout, remote work, and lack of shared meeting spaces. A poor physical setup can hinder spontaneous team dialogue and limit communication and collaboration. Open-plan offices can enhance their overall communication effectiveness, while private offices or remote work environments require more structured communication methods.
Gossip and Rumors
Gossip and informal news can distort the original message, leading to confusion, reduced trust, and poor organizational behavior. Leadership must address these barriers by promoting a culture of transparent communication and discouraging misinformation.
Lack of Feedback and Active Listening
Without feedback, communication within the organization becomes one-way and less effective. Encouraging active listening, two-way dialogue, and performance appraisal discussions is essential for effective communication within an organization. This helps identify misunderstandings and allows employees to clarify their perception of a message.
Organizational Barriers Examples
- A company with multiple management layers delays project approvals, leading to missed business goals.
- Departments that don’t share client feedback, causing duplicate work or missed opportunities.
- Remote teams using different technology platforms, making it hard to coordinate projects.
- Employees ignoring important emails due to information overload.
- Cultural misunderstandings affecting team morale and organizational behavior.
Effect of Communication Barriers on the Workplace

Barriers to communication can significantly harm organizational performance and overall organizational effectiveness. These barriers can lead to:
- Decreased productivity due to duplicate work or missed instructions.
- Low employee morale when staff feel left out or misunderstood.
- Poor decision-making because of incomplete or unclear information.
- High turnover as employees seek better communication environments elsewhere.
- Reduced innovation when teams are not able to share ideas or feedback freely.
How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Communication
Improving communication within the organization is essential for effective teamwork and organizational performance. Here are some strategies to break down barriers and enhance communication and productivity:
Foster Open Communication Channels
Encourage open dialogue at all levels. Use transparent communication channels such as regular team meetings, feedback sessions, and easy-to-access digital platforms.
Clarify Communication Policies
Establish clear communication policies outlining preferred communication methods, timing, and protocols for information sharing.
Simplify Language and Avoid Jargon
Use simple, clear language in emails, messages, and reports. Avoid jargon and technical terms unless everyone understands them.
Leverage Technology Effectively
Choose and train employees on the right telecommunications tools, such as telephone, video conferencing, and instant messaging. Ensure all information is easy to find and accessible to everyone.
Combat Information Overload
Send only essential information and group related updates together. Regularly review communication practices to avoid overwhelming employees with too many messages or news updates.
Break Down Departmental Silos
Promote cross-functional teams and encourage collaboration between departments. This approach enhances organizational communication and helps teams align with company goals.
Provide Communication Skills Training
Offer training sessions on active listening, clear writing, and effective dialogue. This helps everyone in the company improve their communication and collaboration skills.
Enhance Leadership and Management Support
Leadership should model effective communication within the organization by providing timely feedback, clear instructions, and supporting employee engagement.
Address Psychological Barriers
Create a supportive environment where employees feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and emotions. Recognize the importance of employee morale and mental well-being.
Monitor and Improve Communication Effectiveness
Use surveys, performance appraisals, and research (such as studies by Gallup, Inc.) to measure and improve overall communication effectiveness.
Conclusion
Barriers to communication can manifest in any workplace, but understanding organizational barriers is crucial for effective communication within an organization. These barriers can arise due to structure, culture, technology, or individual behavior, and can significantly impact communication and productivity. By recognizing the causes of organizational barriers, setting clear communication policies, and using effective communication methods, companies can overcome these barriers and enhance their overall communication effectiveness.




